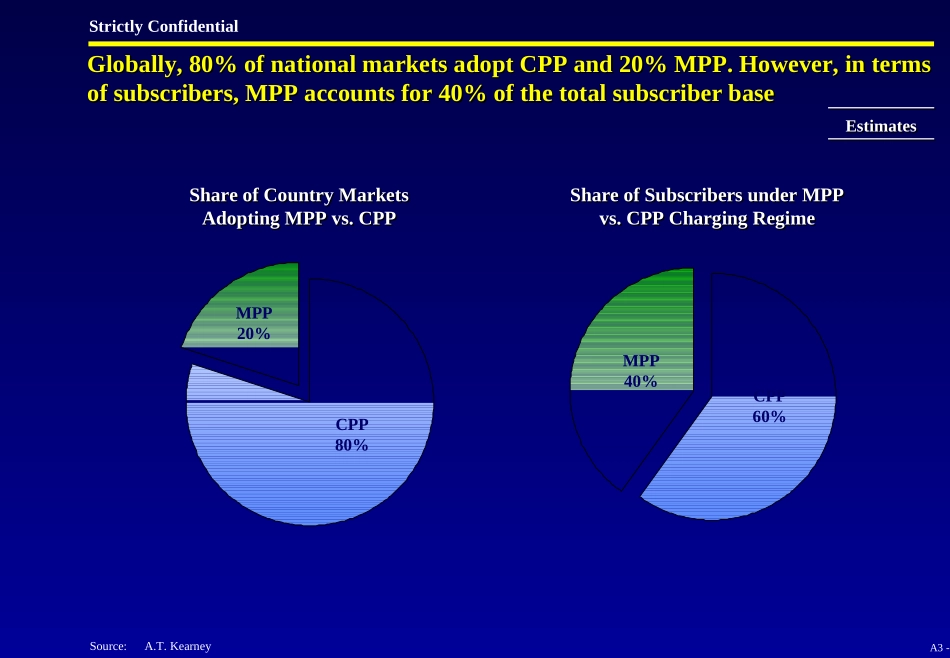
A3-1StrictlyConfidentialA1.IndustryAttractivenessAnalysisA2.OperatorSWOTAnalysisA3.CPPvs.MPPChargingRegimeA4.ProductStrategy–VerticalSolutionsA5.ProductStrategy–CustomerInterviewsA6.MarketAnalysis–byIndustryA7.MarketAnalysis–byGeographyA8.MarketSurveyReportAppendixAppendixA3-2StrictlyConfidentialTherearetwofundamentalchargingregimesformobileservices,MobilePartyPays(MPP)andCallingPartyPays(CPP)Therearetwofundamentalchargingregimesformobileservices,MobilePartyPays(MPP)andCallingPartyPays(CPP)CPPMPPDefinitionThepersoninitiatingacallpaystheentirecostofthecallBoththecallingpartyandthemobilerecipientpaysforaphonecallKeyRegulatoryComplicationUnderaCPPregime,thereislittlecompetitivepressureonmobileoperatorstoensurethatMobileTerminationRates(MTR)arekeptatreasonablelevels.Theresultmaybeexcessiveincreasesinpricesforendcustomers.ThecommonremedyisregulatoryrequirementtoimplementcostbasedMTRsforallmobileoperators(e.ginseveralEuropeanmarkets)TheMPPtendtohaveanegativeimpacton:WirelesspenetrationandusagePricetransparencyProductdevelopment(mainlydata)Impactvaryaccordingtolocalconditions,butempiricalevidenceindicatesthatregulatorymeasuresarerequiredtoensurethatundesiredeffectsoftheMPPregimeareavoidedSource:A.T.KearneyA3-3StrictlyConfidentialGlobally,80%ofnationalmarketsadoptCPPand20%MPP.However,intermsofsubscribers,MPPaccountsfor40%ofthetotalsubscriberbaseGlobally,80%ofnationalmarketsadoptCPPand20%MPP.However,intermsofsubscribers,MPPaccountsfor40%ofthetotalsubscriberbaseShareofCountryMarketsAdoptingMPPvs.CPPShareofCountryMarketsAdoptingMPPvs.CPPCPP80%MPP20%ShareofSubscribersunderMPPvs.CPPChargingRegimeShareofSubscribersunderMPPvs.CPPChargingRegimeCPP60%MPP40%EstimatesEstimatesSource:A.T.KearneyA3-4StrictlyConfidentialThetwochargingregimesofferbothadvantagesanddisadvantagestocustomersandoperatorsImpactonOperatorsCPPMPPAdvantages•Increaseinpenetrationandusage•MobilecarrierscancollectMTRfromfixed-linecarriers•Pricingmechanismsuitablefordata,suchas“alwayson”function(in3Genvironment)•Formobilecarriers,abletochargeforincomingminutesaswellasoutgoingminutes•Pricingmechanismnotsuitablefordataproductsandservices•Forfixed-linecarriers,noneedtopayMTRtomobilecarriersDisadvantages•Notabletochargecustomersforincomingcalls•Mayresultinexcessiveterminationrateschargedbyoperators(empiricalevidenceindicatethattheincidenceofhighMTRisagreaterproblem)•Assomemobilephonesareoftenturnedoff,lesscallswillbeputthrough,resultinginlowerusage•Depressespenetration,sincenotabletoexplorethemorepricesensitivemarketsegmentAssessmentofMPPvs.CPPChargingRegime–ImpactonOperatorsAssessmentofMPPvs.CPPChargingRegime–ImpactonOperatorsSource:A.T.Kearney,OECD,IDAA3-5StrictlyConfidentialThetwochargingregimesofferbothadvantagesanddisadvantagestocustomersandoperators(continued)ImpactonCustomersCPPMPPAdvantages•Improvedpricetransparencyandcontrol•Easiertoreachmobileuserssincemobilephonesaremorelikelytobeturnedon•Equalchargeforfixed-to-mobileasfixed-to-fixedcalls•NoexcessivecostpassedonthroughintroductionofMTRDisadvantages•Increaseinfixedtomobileprice(passedonMTR)•Difficultyincontrollingphonecostsiffixed-to-mobileandfixed-to-fixedarechargedatdifferentrates(notaseriousissueinChinaasphonenumbersareeasilydiscernable)•Havetopayfor“wrongnumbers”or“pushedcalls”•Perceivedhighermobilephonebillsduetopayingforboth...